Ying (Maggie) Chen, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Nephrology
- Phone: 314-362-7603
- Fax: 314-747-5213
- Email: ychen32@nospam.wustl.edu
Related Links
Location
Patients seen at
Center for Advanced Medicine
- Physical Address: 4921 Parkview Place, Saint Louis, MO, United States
-
Mailing Address:
4921 Parkview Place
Suite C, 5th Floor
St. Louis, MO 63110 - Phone: 314-362-7603
- Fax: 314-747-2460
Mailing Address
Division of Nephrology
-
Mailing Address:
660 S. Euclid Ave., CB 8126
St. Louis, MO 63110
Dr. Chen in the news:
- Dr. Maggie Chen Receives UAB-UCSD O’Brien Center Pilot Award
- New Nanotechnique Monitors ER Stress Biomarker for ADTKD
- Ying Maggie Chen Speaks at Yale Symposium
- Ying Maggie Chen Serves on ASN Grants Review Committee
- Ying Maggie Chen Appointed to FACA Nephrology Subcommittee
- Ying Maggie Chen Awarded NU GoKidney Grant
- Dr. Maggie Chen Receives $1.8M Department of Defense Grant to Develop Treatment for FSGS
- Dr. Ying Maggie Chen Awarded $300K Mallinckrodt Challenge Grant
- Ying Maggie Chen Receives Center for Drug Discovery Investigator Matching Grant
- Dr. Maggie Chen and Yeawon Kim Honored at OTM’s Annual Celebration of Inventors
Education
- Doctor of Medicine: Shanghai Medical University Shanghai, China Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg School of Medicine Erlangen, Germany
- PhD Cell and Developmental Biology: Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN
- Residency, Internal Medicine: Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO
- Fellowship, Nephrology: Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO
Board Certifications
- American Board of Internal Medicine, 2008
- American Board of Nephrology, 2010
Recognition
Honors and awards
2003
Dissertation Enhancement Grant, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
2007
NIH Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA, T32)
2010
K08 Clinical Scientist Development Award, NIH/NIDDK
2011
P30 (Pilot and Feasibility Grant), NIH/NIDDK
K Award, Combined Annual Meeting of CSCR (Central Society for Clinical Research) and MWAFMR (Midwestern Section of the American Federation for Medical Research)
2013
Faculty Scholar Award, Children’s Discovery Institute of Washington University and St. Louis Children’s Hospital
The Halpin Foundation-American Society of Nephrology for Kidney Research Grant
2015
Clinical Scientist Development Award, Doris Duke Charitable Foundation
Early Career Development Award, Central Society for Clinical and Translational Research (CSCTR)
K Award, CSCTR and MWAFMR
Career Development Award, Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE)
R03 grant, NIH/NIDDK
2016
Renal Translational Innovation Grant, Washington University Division of Nephrology
2017
R01, NIH/NIDDK
Children’s Discovery Institute hPSC Core Pilot Grant
Clinical Interests
Primary nephrotic syndromes including focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy and minimal change disease; renal thrombotic microangiopathy; acid-base and electrolyte disorders.
Research Interests
Proteinuria; Podocytes; Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress; Renal Fibrosis; Endothelial Cells
Research Description: We are interested in understanding the molecular mechanisms of primary nephrotic syndrome. All strata of the glomerular capillary wall including glomerular basement membrane (GBM), podocytes and endothelial cells operate in a synchronic and integrated manner to maintain the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB). Defects in GFB may cause proteinuria. Ongoing research is focused on two main areas:
Podocyte ER stress and primary nephrotic syndrome (NS)
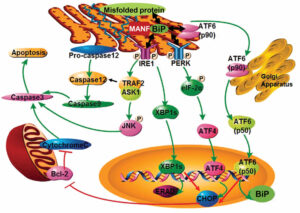
There have been seminal advances in our understanding of the GFB and pathogenesis of proteinuria with major discoveries of podocyte-specific gene mutations in human NS patients. The leading mutated genes identified in NS with genetic basis are NPHS1, NPHS2, WT-1, and LAMB2 encoding laminin b2. LAMB2 is a component of laminin-521, the major laminin in the mature GBM. Although LAMB2 null mutations cause Pierson syndrome manifesting as severe congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS) and significant extrarenal defects, certain LAMB2 missense mutations, including R246Q and C321R, cause CNS with mild extrarenal features. To investigate the mechanisms whereby these missense mutations cause proteinuria, we have developed both cell and transgenic/knockout mouse models with the engineered R246Q or C321R mutation, which recapitulate human NS. Our studies show that both mutations inhibit secretion of laminin-521 from podocytes to the GBM. Furthermore, for the first time in vivo, we demonstrate that the C321R mutant protein induces podocyte ER stress, activates the ER stress-specific apoptotic signal C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and causes podocyte injury before the occurrence of significant proteinuria. Currently, we are using a combination of stably transfected cell lines, transgenic and knock-out animal models and human patient samples to investigate the role of podocyte ER stress in primary NS with a major emphasis on focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. These approaches will enable us to delineate the podocyte ER stress signaling cascades, identify novel biomarkers, and investigate mechanism-based therapies.
Angiopoietin/Tie2 signaling and kidney diseases
Angiopoietins are a family of vascular growth factors. Ang-1 is a 70-kDa glycoprotein secreted by podocytes/renal tubular cells and activates endothelial tyrosine kinase receptor Tie2 in kidney. Ang-1/Tie2 signaling plays an important role in endothelial cell (EC) survival and EC-pericyte stabilization in response to microvascular stress. Moreover, Ang-1 and Ang-2 operate as important agonist/antagonist in both angiogenesis and inflammation. However, their roles in kidneys are not yet well defined. By utilizing an inducible glomerular or renal-tubular specific transgene system, cell biology, biochemistry and state-of-the-art imaging techniques, we are investigating how the locally altered ratio of Ang-1/Ang-2 affects a variety of kidney diseases.
Publications
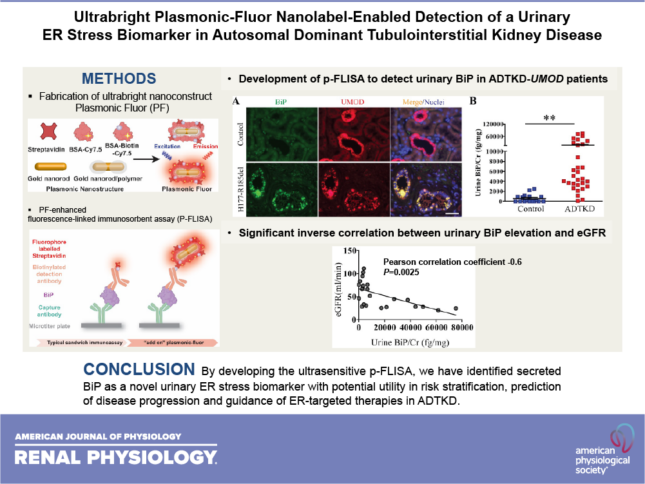
Kim Y, Wang ZY, Li C, Kidd K, Wang YX, Johnson B, Kmoch S, Morrissey J, Bleyer A, Duffield JS, Singamaneni S, Chen Y. Ultrabright plasmonic-fluor nanolabel-enabled detection of a urinary ER stress biomarker in autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 321(2):F236-F244, 2021
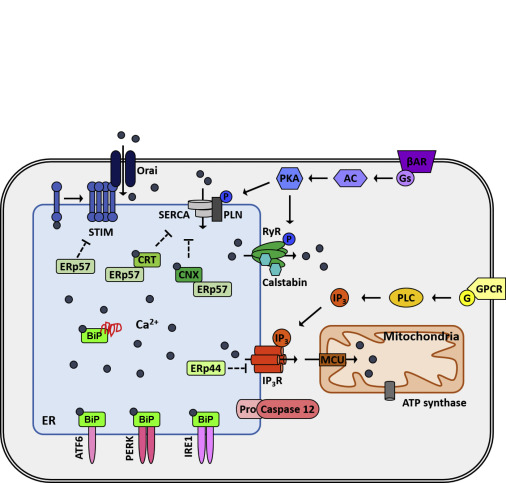
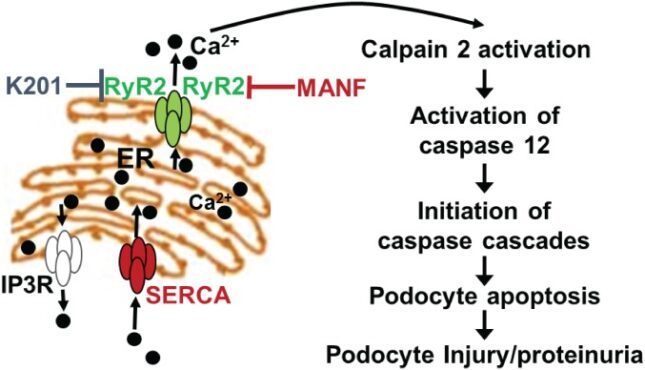
Park SJ, Li C, Chen Y. Endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis in kidney disease: pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Am J Pathol 191(2):256-265, 2021 PMCID: PMC7863132
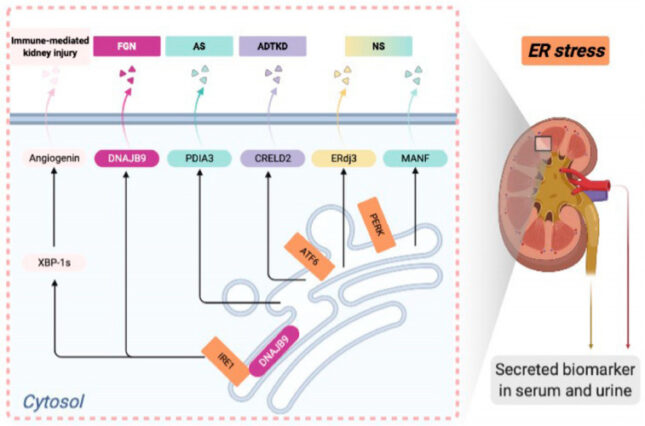
Li C, Chen Y. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated biomarkers for molecular phenotyping of rare kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(4), 2021 PMCID: PMC7926397
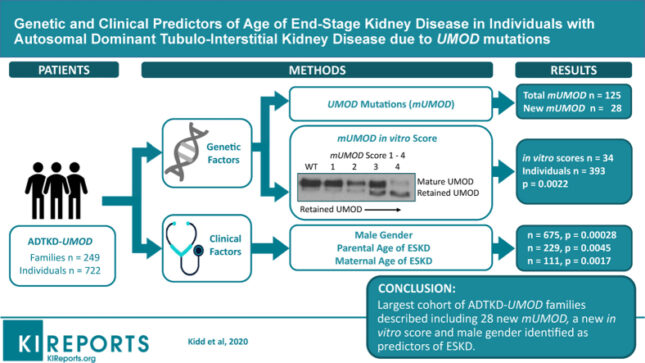
Kidd K, Vyletal P, Schaeffer C, Olinger E, Johnson E, Živná M, Jorge SC, Calado JT, Torres RJ, Lhotta K, Steubl D, Gale DP, Gast C, Gombos E, Robins V, Taylor A, Martin L, Ainsworth H, Chen Y, Almeida JR, Fernandes de Souza C, Silvera CS, Raposeiro R, Hodanova K, Votruba M, Vrbacká A, Divers J, Scolari F, Devuyst O, Rampoldi L, Kmoch S, Bleyer A. Genetic and clinical predictors of age of end-stage kidney disease in individuals with autosomal dominant tubulo-Interstitial kidney disease due to UMOD mutations. Kidney Int Rep 5(9): 1472-1485, 2020 PMCID: PMC7486199
Park SJ, Kim Y, Yang SM, Henderson MJ, Yang W, Lindahl M, Urano F, Chen Y. Discovery of novel endoplasmic reticulum calcium stabilizers to rescue ER-stressed podocytes in nephrotic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(28): 14154-14163, 2019 PMCID: PMC6628787
Highlighted by Nature Reviews Nephrology in July 2019 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-019-0180-1
Park SJ, Kim Y, Chen Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and monogenic kidney diseases in precision nephrology. Pediatr Nephrol (https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4031-2), 2018 PMID: 30099615
Kim Y, Park SJ, Manson SR, Carlos M, Kidd K, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Perry R, Liapis H, Kmoch S, Parikh CR, Bleyer AJ, Chen Y. Elevated urinary CRELD2 is associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated kidney disease. JCI Insight 2(23): e92896 2017
Kim Y, Park SJ, Chen Y. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF), a new player in endoplasmic reticulum diseases: structure, biology and therapeutic roles. Transl 188: 1–9 2017 [Featured New Investigator Series]
Mutneja A, Cossey LN, Liapis H, Chen Y. A rare case of renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated with Castleman’s disease. BMC Nephrol 18: 57, 2017.
Kim Y, Lee H, Manson SR, Lindahl M, Evans B, Miner JH, Urano F, Chen Y. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor as a urine biomarker for endoplasmic reticulum stress-related kidney diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 27: 2974-2982 2016 PMCID: PMC5042655
Singh S, Manson SR, Lee H, Kim Y, Liu T, Guo QS, Geminiani JJ, Austin PF, and Chen Y. Tubular overexpression of angiopoietin-1 attenuates renal fibrosis. PLOS ONE 11(7): e0158908 2016
Chen Y, Liapis H. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: molecular genetics and targeted therapies. [Corresponding author] BMC Nephrol 16: 101, 2015
Chen Y, Zhou YF, Go G, Marmerstein JT, Kikkawa Y, Miner J. Laminin β2 gene missense mutation produces endoplasmic reticulum stress in podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24: 1223-1233 2013
Chen Y, Marcos LA, Liapis H, Steinberg TH, Morrison AR. An unusual cause of membranous glomerulonephritis in a patient with HIV. Int Urol Nephrol. 44(3): 983-6 2012
Chen Y, Miner J. Glomerular basement membrane and related glomerular disease. Transl 160: 291–297 2012 [Corresponding author, Featured New Investigator Series]
Chen Y, Kikkawa Y, Miner J. A missense LAMB2 mutation causes congenital nephrotic syndrome by impairing laminin secretion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22: 849-858 2011 [Cover illustration]
Chen Y, Donnelly E, Kobayashi H, DeBusk LM and Lin PC. Gene therapy targeting the Tie2 function ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 52(5): 1585-1594 2005
[Editorial comments]: Pap T and Distler O. Linking angiogenesis to bone destruction in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 52(5): 1346-1348
Chen JX, Chen Y, DeBusk LM, Lin W, Lin PC. Dual functional roles of Tie2/angiopoietin in TNF-alpha-mediated angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 287(1): H187-195 2004
DeBusk LM, Chen Y, Nishishita T, Chen J, Thomas JW, Lin PC. Tie2 receptor tyrosine kinase, a major mediator of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 48(9): 2461-2471 2003
Chen Y, Rosloniec E, Price J, Boothby M, Chen J. Constitutive expression of Bcl-xL in the T lineage attenuates collagen-induced arthritis in Bcl-xL transgenic mice. Arthritis Rheum. 46(2): 514-521 2002
Chen Y, Rosloniec E, Goral MI, Boothby M, Chen J. Redirection of T cell effector function in vivo and enhanced collagen-induced arthritis mediated by an IL-2Rb/IL-4Ra chimeric cytokine receptor transgene. Immunol. 166(6): 4163-4169 2001